
Total Heat Exchanger: The Latest and Most Detailed Revelation
2023-10-24 | Heat Exchanger
1. What is a Total Heat Exchanger?
A Total Heat Exchanger, also referred to as a Total Heat Recovery Unit or simply Total Heat Exchanger, is a device used for heat recovery purposes. It is typically employed in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. Its primary function is to transfer heat and humidity between indoor and outdoor environments, aiming to achieve energy conservation and improve indoor air quality.
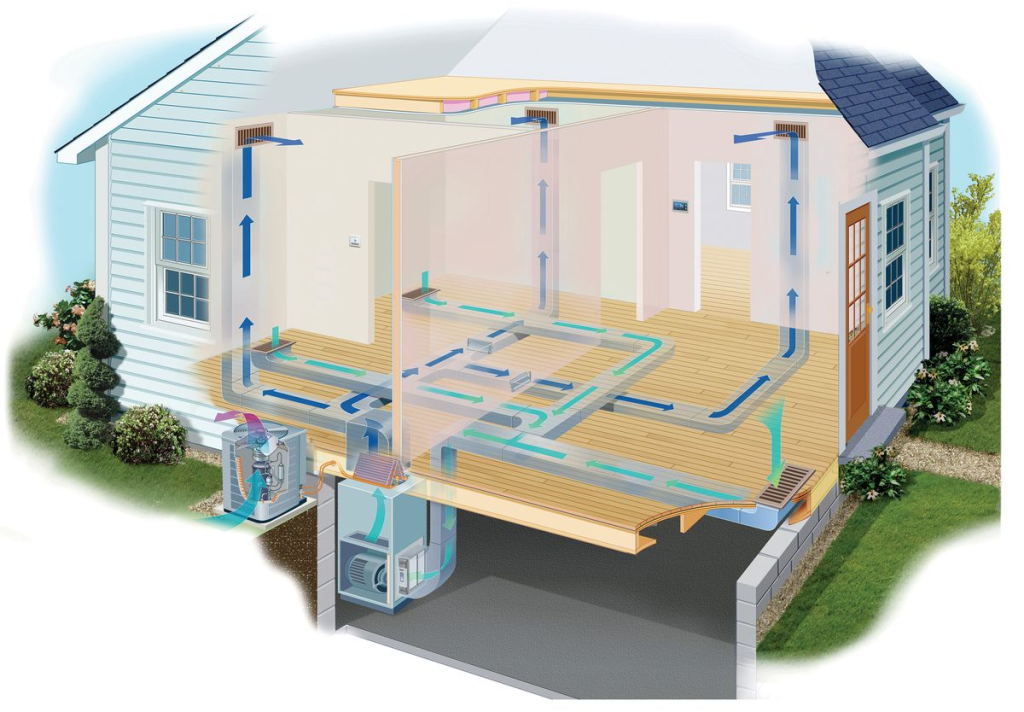
2. Working Principle of Total Heat Exchanger:
Through a special heat exchange medium (usually a heat exchange membrane or a wheel-type heat exchanger), it achieves the transfer of heat and humidity between indoor and outdoor environments. During the cold season, when the outdoor air temperature is lower, it can recover the heat and humidity from the indoor exhaust air and transfer these energies to the fresh indoor air, thereby reducing the heating load and maintaining indoor humidity. In the hot summer, it transfers the heat and humidity from the outdoor hot and humid air to the exhaust air, reducing the cooling load.
3. Key Advantages of Total Heat Exchanger in HVAC Systems:
1. Energy Savings: Total heat exchangers recover heat between indoor and outdoor environments, allowing heating and cooling systems to use energy more efficiently. This significantly reduces the energy consumption and lowers energy costs.
2. Reduced Energy Waste: By avoiding direct discharge of indoor and outdoor heat and humidity into the environment, total heat exchangers reduce energy waste and enhance system efficiency.
3. Improved Indoor Air Quality: Total heat exchangers help filter and purify the incoming fresh air, improving indoor air quality. They also help maintain appropriate humidity levels, preventing indoor air from becoming too dry or too humid.
4. Lower Humidity Load: In summer, total heat exchangers transfer outdoor humidity to the exhaust air, reducing the humidity load on the cooling system and improving cooling efficiency.
5. Comfort Maintenance: By maintaining indoor air quality, temperature, and humidity within comfortable ranges, total heat exchangers contribute to creating a more comfortable indoor environment, enhancing living and working comfort.
6. Environmental Compliance: Due to their contribution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption, total heat exchangers help meet environmental standards and sustainable development goals.
7. Extended Equipment Lifespan: By reducing the load and operation time of heating and cooling systems, total heat exchangers minimize equipment wear, extending the lifespan of the equipment.
8. Economic Viability: While total heat exchangers may require initial investment, they typically offer long-term economic returns through energy cost savings and extended equipment lifespan.
4. Comparison between Total Heat Exchanger and Fresh Air Fan in HVAC Systems:
Advantages of Total Heat Exchanger:
Energy Recovery: Total heat exchangers can recover heat and humidity between indoor and outdoor environments, improving the system's energy efficiency. This reduces the energy consumption of heating and cooling systems, saving energy costs.
Reduced Energy Waste: By avoiding direct discharge of indoor and outdoor heat and humidity into the environment, total heat exchangers reduce energy waste, enhancing system efficiency.
Improved Indoor Air Quality: Total heat exchangers assist in filtering and purifying incoming fresh air, thereby improving indoor air quality. They also help maintain appropriate humidity levels, preventing indoor air from becoming excessively dry or humid.
Lower Humidity Load: In summer, total heat exchangers can transfer outdoor humidity to the exhaust air, reducing the humidity load on the cooling system and improving cooling efficiency.
Comfort Maintenance: By maintaining indoor air quality, temperature, and humidity within comfortable ranges, total heat exchangers contribute to creating a more comfortable indoor environment, enhancing living and working comfort.
Disadvantages of Total Heat Exchanger:
High Initial Investment: Total heat exchangers typically require a significant initial investment, making them relatively costly compared to simple fresh air fans.
Complex Maintenance: The design of total heat exchangers is relatively complex and may require more maintenance and cleaning to ensure their performance. This complexity can increase maintenance costs and workload.
Advantages of Fresh Air Fan:
Low Cost: Fresh air fans generally have a lower initial cost compared to total heat exchangers. They provide an economical way to introduce fresh air.
Simplified Maintenance: Fresh air fans usually require simpler maintenance, involving less cleaning and upkeep.
Wide Applicability: Fresh air fans are suitable for environments that do not require advanced heat and humidity recovery functions, such as offices, shops, small residences, etc.
Disadvantages of Fresh Air Fan:
Energy Waste: Fresh air fans typically do not recover heat and humidity when introducing outdoor air, potentially leading to higher heating and cooling costs.
Lack of Humidity Control: Fresh air fans usually cannot effectively control indoor humidity, potentially causing indoor air to become excessively dry or humid in certain situations.
Conclusion:
The choice between a total heat exchanger and a fresh air fan depends on specific needs and application scenarios. If energy savings and advanced air treatment are primary concerns, a total heat exchanger might be more suitable. If cost is a primary consideration and there is a lower requirement for energy recovery, a fresh air fan might be a better fit. Often, some systems may combine both to balance energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness.